Using the Simple Constant Growth DCF to Assess Market Capitalization Rate
Valuing a company accurately is crucial for making informed investment decisions, and among the various methods available, the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model stands out as a fundamental approach. One of its simpler yet effective variants is the Simple Constant Growth DCF model. This model, also known as the Gordon Growth Model or the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), provides insights into how to determine a company’s market capitalization rate. Let’s explore how this model works and what it means for assessing market value.
What is the Simple Constant Growth DCF Model?
The Simple Constant Growth DCF model is designed to value a company’s stock by assuming a perpetual, constant growth rate in dividends or free cash flows. It’s a straightforward method that hinges on a few key assumptions but offers powerful insights into a company’s value.
Understanding the Basics
In this model, dividends are treated as a perpetuity, meaning they continue indefinitely. The present value of this perpetuity, with a discount rate ![]() and a growth rate
and a growth rate ![]() , can be calculated using the formula:
, can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
For equity, cash flow is equivalent to dividends. Thus, the present value of all future dividend streams can be expressed as:
![]()
where:
– ![]() = Current stock price (or value of the company)
= Current stock price (or value of the company)
– ![]() = Dividend just paid
= Dividend just paid
– ![]() = Constant growth rate of dividends (or free cash flows)
= Constant growth rate of dividends (or free cash flows)
– ![]() = Required rate of return (market capitalization rate)
= Required rate of return (market capitalization rate)
To find the market capitalization rate ![]() , rearrange the formula:
, rearrange the formula:
![]()
Estimating the Growth Rate 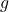
Estimating the growth rate ![]() is crucial for applying the Simple Constant Growth DCF model effectively. This growth rate can be derived from various sources:
is crucial for applying the Simple Constant Growth DCF model effectively. This growth rate can be derived from various sources:
1. Historical Growth Rates:
– Analyze past dividend or earnings growth to project future growth rates.
2. Future Projections:
– Utilize projections from financial analysts or company forecasts.
3. Plowback Ratio and ROE:
– The plowback ratio represents the percentage of earnings reinvested in the business after paying dividends. It is calculated as:
![]()
– Return on Equity (ROE) is the ratio of earnings to book value. Growth rate can be expressed as:
![]()
This formula links dividend growth to the company’s reinvestment strategy and profitability.
Implications and Limitations
While the Simple Constant Growth DCF model is valuable, it comes with limitations:
1. Assumption of Constant Growth:
– The model assumes a perpetual, constant growth rate, which may not be realistic for all companies, especially high-growth or volatile stocks.
2. Sensitivity to Inputs:
– Small variations in the growth rate or current stock price can significantly affect the calculated market capitalization rate.
3. Suitability:
– This model works best for companies with stable and predictable dividend policies. It might not be suitable for companies in highly volatile industries or those that do not pay dividends.
4. Market Capitalization Rate Across Stocks:
– It’s often useful to compute the market capitalization rate for a group of similar stocks and take the average to mitigate individual stock anomalies.
Conclusion
The Simple Constant Growth DCF model provides a clear framework for estimating a company’s market capitalization rate, making it an essential tool for investors. By understanding its assumptions and limitations, you can use this model effectively to gauge a company’s value and make more informed investment decisions. Remember, while this model offers a valuable perspective, it should be complemented with other valuation methods for a comprehensive analysis.




